History of Renewable Energy Development in Brazil
Brazil has a long and fascinating history with renewable energy, marked by innovation, challenges, and significant achievements.
Here's a timeline of key milestones:
Early Developments:
- Pre-20th Century: Traditional uses of renewable energy for cooking, heating, and water power existed throughout Brazil's history.
- Early 20th Century: Hydropower projects begin, with initial installations primarily for industrial use.
20th Century Expansion:
- 1970s: Oil shocks prompt diversification efforts, leading to a focus on ethanol made from sugarcane. The Proálcool program incentivizes ethanol production, making Brazil a leader in biofuels.
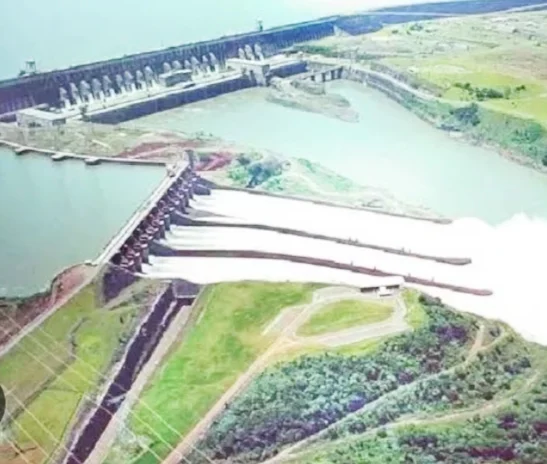
- 1980s: Construction of the world's largest hydroelectric dam, Itaipu, further solidifies hydropower's dominance.
- 1990s: The first wind turbine and small-scale solar projects are installed, marking the initial diversification beyond large hydro and ethanol.
21st Century Growth and Diversification:
- 2000s: The Proinfa program provides substantial incentives for renewable energy development, leading to significant growth in wind and solar power.
- 2010s: Focus expands to other renewable sources like biomass and biogas. Brazil becomes a global leader in installed wind power capacity.
- 2020s: Continued growth in wind and solar, with increasing focus on grid integration, distributed generation, and energy storage.
Key Points:
- Early focus on hydropower and then ethanol, followed by recent diversification into wind and solar.
- Government incentives have played a crucial role in driving growth.
- Sustainability concerns with large hydro projects add complexity to the landscape.
- Brazil remains a global leader in renewables, with continued potential for expansion.
Additional Notes:
- The history of renewable energy in Brazil is intertwined with socio-economic factors, like oil crises and rural development goals.
- Technological advancements and decreasing costs have enabled the growth of newer renewable sources like wind and solar.
- Challenges exist regarding environmental impacts, social displacement, and grid modernization as the sector evolves.
Renewable Energy Sources in Brazil
Brazil stands tall as a global leader in renewable energy, generating a staggering 80% of its electricity from clean sources. This remarkable achievement is made possible by a diverse mix of renewable energy players, each with its own fascinating story and impact:
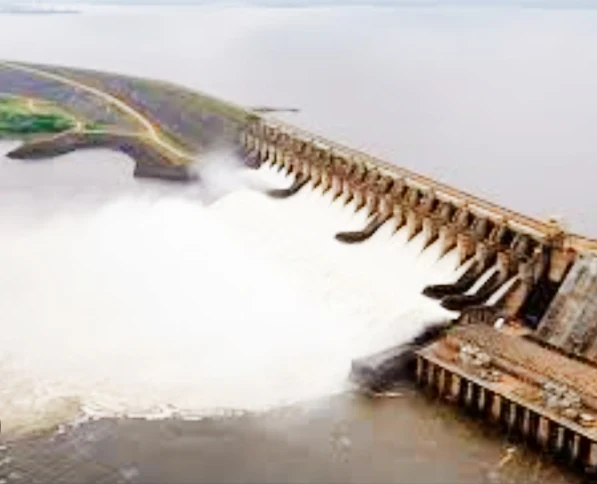
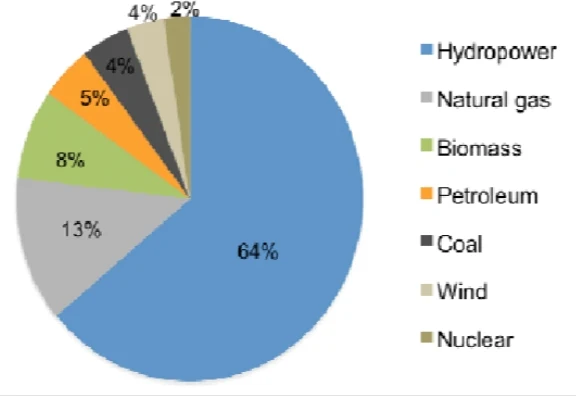
1. Hydropower: The undisputed champion, hydropower remains king, responsible for a whopping 65% of Brazil's electricity generation. The mighty Amazon River and its tributaries provide immense potential, harnessed by colossal hydroelectric dams like the iconic Itaipu. While clean, large dams raise concerns about environmental impact and social displacement, additionally making the system vulnerable to droughts.
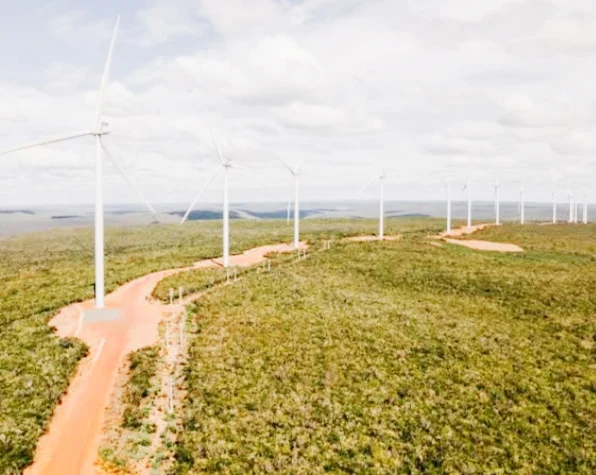
2. Wind Power: Experiencing a meteoric rise, wind energy now contributes 11% of the nation's electricity. With over 890 wind farms blanketing the landscape, Brazil boasts the 11th position in global wind power production. Favorable wind conditions, particularly in the Northeast region, make the country a prime location for harnessing this powerful resource.
3. Solar Power: Basking in abundant sunshine, solar power is experiencing rapid growth, currently holding a 2.5% share of the energy mix. Projected to play a more significant role in the future, its decentralized nature empowers communities and individuals with rooftop installations, offering a unique advantage over large hydro projects.
4. Bioenergy: A global leader in biofuels, Brazil holds the second spot in ethanol production, derived from sugarcane. Blended with gasoline, ethanol reduces reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, biomass, encompassing organic matter like wood waste and agricultural residues, is increasingly used for heat and electricity generation.
5. Other Renewables: Emerging players like geothermal, biogas, and small hydropower contribute a smaller but growing share, adding resilience and sustainability to the energy mix.
The Future Beckons:
Brazil's ambition doesn't stop here. They aim to expand the share of renewables, setting ambitious targets for wind, solar, and biomass. Research and development efforts focus on grid integration, energy storage, and advanced technologies for further diversification. Balancing energy needs with environmental and social responsibility remains crucial for a sustainable renewable energy future.
As technology advances and challenges are addressed, Brazil's renewable energy landscape promises to be even more groundbreaking, solidifying its position as a global leader in the clean energy revolution.
Statistical Snapshot of Renewable Energy in Brazil
Dominant Force: Hydropower
- Contribution: 65% of electricity generation
- Significance: Mighty dams like Itaipu utilize the Amazon's potential, but raise concerns about environmental impact, social displacement, and drought vulnerability.
Wind Power on the Rise
- Contribution: 11% of electricity generation
- Growth: Rapidly expanding with over 890 wind farms, ranking Brazil 11th globally.
- Favorable Conditions: Strong and consistent winds, particularly in the Northeast region, make Brazil a prime location.
Solar Power's Bright Future
- Contribution: 2.5% of electricity generation
- Potential: Abundant sunshine fuels rapid growth, with projections for a more significant role.
- Decentralization: Unlike large hydro, solar offers individual and community empowerment through rooftop installations.
Bioenergy: A Leading Player
- Contribution:
- World's second-largest producer of ethanol (derived from sugarcane, blended with gasoline to reduce fossil fuel reliance)
- Increasing use of biomass for heat and electricity generation (organic matter like wood waste and agricultural residues)
Other Renewables:
- Smaller but growing share from emerging players like geothermal, biogas, and small hydropower.
- Enhance the energy mix's resilience and sustainability.
Data-Driven Insights:
- Electricity Generation from Renewables: 526.10 billion kWh in 2024 (projected to reach 602.84 billion kWh by 2028)
- Annual Growth Rate: 2.69% (CAGR 2024-2028) for renewable energy electricity generation
- Installed Capacity:
- Wind: 21.5 GW (2022)
- Solar: 16.9 GW (2022)
- Biomass: 15.2 GW (2022)
Future Outlook:
Brazil aims to:
- Expand the share of renewables in the energy mix
- Set ambitious targets for wind, solar, and biomass
- Foster innovation in grid integration, energy storage, and advanced technologies
By addressing environmental and social concerns while embracing technological advancements, Brazil is poised to solidify its position as a global leader in the renewable energy revolution.
Remember: These statistics paint a dynamic picture, and data may vary depending on the source and timeframe.
Brazil's Renewable Energy Statistics (2022)
| Source | Contribution to Electricity Generation | Installed Capacity | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydropower | 65% | - | Dominant force, concerns about environmental impact and drought vulnerability |
| Wind Power | 11% | 21.5 GW | Rapid growth, favorable wind conditions in Northeast region |
| Solar Power | 2.5% | 16.9 GW | Bright future, decentralized generation potential |
| Bioenergy | - | - | |
| - Ethanol | - | - | World's second-largest producer, reduces fossil fuel reliance |
| - Biomass | - | 15.2 GW | Increasing use for heat and electricity generation |
| Other Renewables | Smaller share | - | Growing players, enhance mix's resilience |
| Total Renewables | 80% | - | Global leader in renewable energy |
Additional Data:
- Electricity Generation from Renewables in 2024: 526.10 billion kWh (projected to reach 602.84 billion kWh by 2028)
- Annual Growth Rate for Renewables (CAGR 2024-2028): 2.69%
Note: Data may vary depending on the source and timeframe.
Hydro Energy in Brazil
Here's some key data on Hydro Energy in Brazil:
Production:
- Share of electricity generation: 66% in 2020 (highest in the world)
- Installed capacity: 105 GW (2022)
- Number of hydroelectric power stations:
- 201 with capacity > 30 MW (total capacity 84,703 MW)
- 476 with capacity 1-30 MW
- 496 micro plants with capacity < 1 MW
- Largest hydroelectric power station: Itaipu Dam (14 GW)
Sources:
- Electricity generation: Hydropower Association, U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)
- Installed capacity: International Hydropower Association
- Hydroelectric power stations: Wikipedia
Additional data:
- Potential for further development: Estimated at 260 GW, mainly in the Amazon Basin.
- Recent development: 300 MW added in 2022 with 15 new plants commissioned.
- Environmental impact: Concerns about deforestation and displacement of communities due to dam construction.
Wind Energy in Brazil
Here's some key data on Wind Energy in Brazil:
Production:
- Share of electricity generation: 11% in 2021 (2nd largest renewable source)
- Installed capacity: 24.62 GW (2023)
- Number of wind farms: 903 (2023)
- Largest wind farm: Chafariz, Rio Grande do Norte (883 MW)
Sources:
- Electricity generation: Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC), Brazilian Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME)
- Installed capacity: GWEC, MME
- Wind farms: Brazilian Association of Wind Power (ABEEólica)
Additional data:
- Rank in global wind energy: 6th (2023)
- Recent development: Record-breaking power generation in 2023, 5 GW new capacity added
- Potential for further development: Estimated at 880 GW, with strong onshore potential in Northeast region
Solar Energy in Brazil
Here's some key data on Solar Energy in Brazil:
Production:
- Share of electricity generation: 2% in 2022 (third largest renewable source)
- Installed capacity: 12.6 GW (2023)
- Number of solar plants: 16,993 (2023)
- Largest solar park: São Miguel do Tapuio, Bahia (576 MW)
Sources:
- Electricity generation: International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), Brazilian Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME)
- Installed capacity: IRENA, MME
- Solar plants: Brazilian Photovoltaic Solar Energy Association (ABSOLAR)
Additional data:
- Rank in global solar energy: 12th (2023)
- Recent development: Strong growth in recent years, with 4.7 GW added in 2023
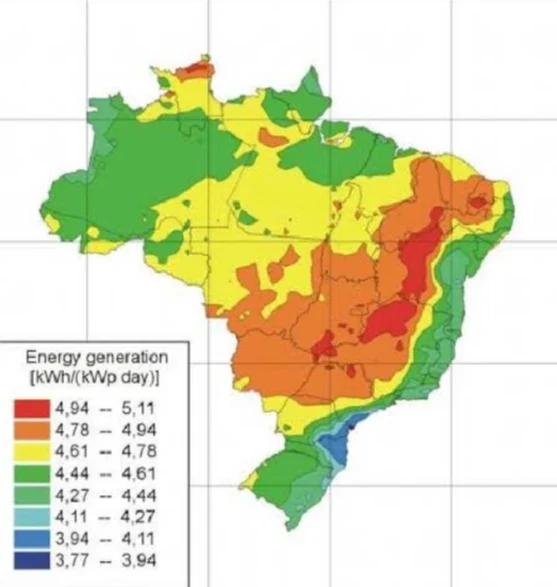
- Potential for further development: Significant, with high solar irradiation levels throughout the country.
- Types of solar installations: Dominated by distributed generation (rooftop) installations, but utility-scale projects are growing.
Environmental impact:
- Considered a clean energy source with minimal land use compared to other renewables. However, manufacturing and disposal of solar panels require careful management.
Comparison with other renewables:
While solar energy currently generates less electricity than hydro and wind in Brazil, it has experienced the fastest growth and has significant potential for further development.
Bioenergy in Brazil: Statistic Data
Bioenergy plays a significant role in Brazil's energy mix, being the dominant renewable source and holding a strong position globally. Here's some key data:
Production:
- Share of electricity generation: 8% in 2022 (third largest source after hydro and wind)
- Installed capacity: 15.3 GW (2022)
- Bioenergy production: 55.8 TWh in 2021 (largest producer globally)
- Breakdown of production:
- Sugarcane ethanol: 85%
- Bagasse: 12%
- Biodiesel: 3%
Sources:
- Electricity generation: Global Bioenergy Statistics (GBS), International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)
- Installed capacity: REN21 Global Status Report, GBS
- Bioenergy production: Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), International Energy Agency (IEA)
Additional data:
- Rank in global bioethanol production: 1st (2022)
- Recent development: Focus on expanding sugarcane-based ethanol production and exploring second-generation biofuels from other biomass sources.
- Potential for further development: Significant, especially in areas like cellulosic ethanol and biogas.
Social and environmental impact:
- Positive contributions to energy security and rural development.
- Concerns about deforestation related to sugarcane expansion, water use, and social impacts on local communities.
Other Renewable Energy Source in Brazil
Beyond the major players like hydro, wind, solar, and bioenergy, Brazil also utilizes other, less prominent renewable energy sources. Here's a brief overview:
Small Hydropower:
- Installed capacity: 5.1 GW (2022)
- Number of plants: 1,397 (2022)
- Primarily utilized in remote areas and contributes to local energy needs.
Biomass Gasification:
- Installed capacity: 100 MW (2022)
- Utilizing agricultural and forestry residues, generating electricity and heat.
- Still in early stages of development but holds potential for expansion.
Geothermal:
- Estimated potential: 30 GW
- Currently no operational plants, but exploratory projects are ongoing.
- Located mainly in the Northeast region.
Ocean Energy:
- Still in nascent stage, with research and pilot projects focused on wave and tidal energy.
- High potential due to extensive coastline, but technological and economic challenges remain.
Hydrogen:
- Early stage of development, focusing on green hydrogen production from renewable sources.
- Potential applications in transportation, industry, and energy storage.
Largest Renewable Energy Company in Brazil
Determining the "largest" renewable energy company in Brazil depends on your definition of "largest." Here are some aspects to consider:
By Installed Capacity:
- Hydropower: Eletrobras dominates this sector, holding 64% of Brazil's electricity generation with mainly hydroelectric plants. However, they also utilize other sources.
- Wind power: CPFL Energias Renovaveis S.A. (CPFL Renovaveis) holds the top spot with over 8.8 GW of installed wind capacity.
- Solar power: This sector is more fragmented, with several companies like Canadian Solar, Lightsource bp, and Atlas Renewable Energy vying for the top position. Their exact rankings may vary depending on specific parameters.
By Market Share (Across All Renewables):
- CPFL Renovaveis emerges again with a significant market share in the combined renewable energy market.
- ENGIE Brazil and Eletrobras Furnas are also major players, especially considering their diverse portfolios involving hydro, wind, and solar.
Other Factors:
- Revenue: Analyzing annual revenue from renewable energy operations could offer a different perspective.
- Project Portfolio: Considering the number and scale of upcoming renewable energy projects might indicate future leadership.
Therefore, pinpointing the absolute "largest" single company can be challenging due to varied definitions and market dynamics. It's best to choose a specific metric (installed capacity, market share, etc.) and search for the relevant leader based on that.
Additionally, remember that the renewable energy landscape in Brazil is evolving rapidly, so rankings could change over time.
The Future of Renewable Energy Development in Brazil: A Promising Outlook
Brazil has already carved a niche as a leader in renewable energy, but the future promises even greater strides. Here's an overview of key trends and factors shaping its development:
Growth Potential:
- Abundant Renewable Resources: Brazil possesses vast potential for wind, solar, biomass, and hydro power, offering a diverse and sustainable energy mix.
- Technological Advancements: Falling costs and improved efficiency of renewable technologies make them increasingly competitive with fossil fuels.
- Government Support: Policies promoting renewable energy auctions, tax incentives, and transmission infrastructure upgrades provide a conducive environment.
- Growing Demand: Increasing energy consumption coupled with environmental concerns fuels demand for clean energy solutions.
Key Areas of Development:
- Wind Power: Expansion expected in the Northeast and Southern regions, potentially doubling installed capacity by 2030.
- Solar Power: Distributed generation (rooftop solar) poised for significant growth, alongside utility-scale projects expanding across various regions.
- Biomass: Continued role expected, focusing on efficiency improvements and diversification beyond sugarcane ethanol.
- Other Renewables: Emerging technologies like ocean energy and bioenergy from waste could contribute to the mix in the long run.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Transmission Infrastructure: Upgrading and expanding the grid is crucial to integrate and distribute renewable energy effectively.
- Financing: Securing long-term investments for large-scale projects remains a challenge, despite initiatives like green bonds.
- Community Engagement: Ensuring social and environmental responsibility in project development is vital for sustainability and community acceptance.
- Innovation and Technological Advancements: Continued research and development in storage solutions, smart grids, and advanced renewable technologies will be key to optimizing the energy system.
The future of renewable energy development in Brazil appears bright. With its substantial resources, supportive policies, and growing market demand, the country is well-positioned to capitalize on this sector's potential. However, addressing challenges like infrastructure gaps, financing, and responsible development will be crucial for sustainable and inclusive progress.