Understanding Extended Reality (XR)
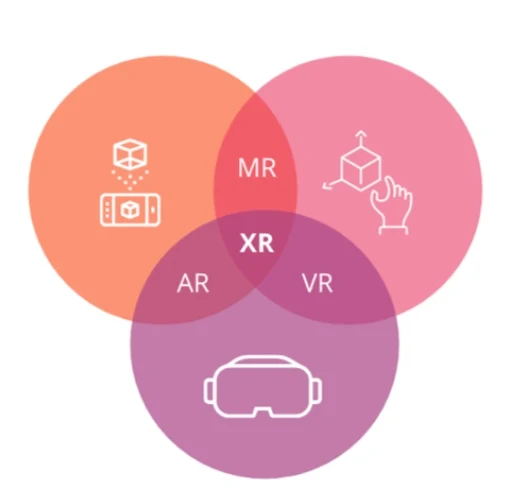
Extended reality (XR) is a broad term encompassing various immersive technologies that alter our perception of the real world. It serves as an umbrella for three primary technologies: virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR). Each technology offers a unique way to interact with digital elements, blurring the lines between the physical and virtual realms.
Current Extended Reality (XR) Projects by Industry
Here's a table showcasing some real-world XR projects across various industries:
| Industry | Project Name | Description | Target Audience | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaming | Pokémon Go (AR) | Mobile game where players capture virtual Pokémon in the real world using their phone's camera. | Mobile gamers | Location-based entertainment, social interaction |
| Healthcare | Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy (VR) | Uses VR simulations to treat phobias and anxiety disorders in a safe and controlled environment. | Patients with phobias and anxiety | Exposure therapy, treatment for mental health conditions |
| Education | Google Expeditions (VR) | VR app that allows students to virtually travel to historical landmarks and natural wonders. | Students, educators | Immersive learning experiences, sparking curiosity and engagement |
| Retail | IKEA Place (AR) | AR app that lets users virtually place furniture in their homes to see how it looks before buying. | Shoppers | Product visualization, informed purchase decisions |
| Architecture & Design | Microsoft HoloLens 2 (MR) | Mixed reality headset used by architects and designers to visualize and interact with 3D models in real-time. | Architects, designers | Collaborative design workflows, improved spatial understanding |
| Manufacturing & Training | Boeing VR Training (VR) | VR simulations used to train aircraft assembly workers on complex procedures. | Manufacturing workers | Safe and realistic job training, improved efficiency |
Please note: This table presents just a few examples, and there are many other exciting XR projects happening across various industries. As XR technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications to emerge in the future.
Table A Comparison of XR Technologies
| Feature | Virtual Reality (VR) | Augmented Reality (AR) | Mixed Reality (MR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environment | Fully immersive, computer-generated world | Overlays digital elements onto the real world | Merges real and virtual worlds, allowing interaction between both |
| Hardware | Head-mounted displays (HMDs) | Smartphones, tablets, AR glasses | HMDs with see-through displays |
| Applications | Gaming, education, training simulations, therapy | Gaming, product visualization, maintenance and repair assistance | Design, education, medical procedures, remote collaboration |
VR Technology
Virtual reality (VR) creates a completely simulated environment that users experience through head-mounted displays (HMDs). VR users can navigate and interact with virtual objects and characters, fostering a sense of presence within the digital world. Applications of VR span various industries, including gaming, education, training simulations, and even therapy.
AR Technology
Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital elements onto the physical world. Users can view these enhancements through smartphone cameras, tablets, or specialized AR glasses. AR offers a more interactive experience compared to traditional screens, allowing users to manipulate virtual objects within their real-world surroundings. AR applications are prevalent in gaming, product visualization, and maintenance and repair assistance.
MR Technology
Mixed reality (MR) merges the real and virtual worlds, enabling real-time interaction between both. MR headsets typically feature see-through displays that allow users to view the physical environment while simultaneously integrating virtual elements. This technology finds applications in design, education, medical procedures, and remote collaboration.
The future of XR holds immense potential for transforming various aspects of our lives. As XR technologies continue to evolve and become more accessible, we can expect even more innovative applications to emerge, shaping the way we learn, work, and interact with the world around us.
Demystifying the World of Extended Reality (XR): A Look at VR, AR, and MR
Types of Extended Reality (XR)
| Type of XR | Description | Hardware | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual Reality (VR) | Creates a fully digital and immersive environment. Users cannot see the real world. | Head-mounted display (HMD) | Gaming, training simulations, therapy exposure |
| Augmented Reality (AR) | Overlays digital elements onto the real world. Users can still see their surroundings. | Smartphone, tablet, AR glasses | Gaming with AR elements, product visualization (e.g., seeing furniture in your room), repair instructions with digital overlays |
| Mixed Reality (MR) | Merges the real and virtual worlds simultaneously. Users can interact with digital objects as if they were in the real world. | Head-mounted display (HMD) with transparent screen | Design (e.g., projecting 3D models onto a workspace), education (e.g., learning anatomy with interactive AR/VR models), medical procedures (e.g., visualizing surgery) |
The world of technology is constantly evolving, blurring the lines between the physical and digital realms. Extended reality (XR) is at the forefront of this innovation, offering a spectrum of immersive experiences that reshape how we interact with the world around us. But with various XR technologies under its umbrella, it can be easy to get confused. This article dives into the three main types of XR – virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) – to help you understand their distinct functionalities and applications.
Virtual Reality (VR): Stepping into a Completely Digital World
Imagine yourself transported to a breathtaking mountain peak or exploring the depths of the ocean – all from the comfort of your living room. VR makes this possible by creating a fully immersive, computer-generated environment. Users wear head-mounted displays (HMDs) that block out the real world and replace it with a virtual one. VR allows for complete user control, enabling them to navigate and interact with virtual objects and characters. This technology has revolutionized various industries, particularly gaming, where users can experience hyper-realistic adventures. VR also finds applications in training simulations for pilots, surgeons, and soldiers, providing a safe and controlled environment to hone their skills. Additionally, VR therapy has shown promise in treating phobias and anxiety disorders by allowing patients to confront their fears in a virtual setting.
Augmented Reality (AR): Enhancing the Real World with Digital Overlays
Unlike VR, AR doesn't replace your surroundings; instead, it augments them. Imagine holding your phone up to see furniture virtually placed in your room before you buy it, or receiving step-by-step repair instructions with digital overlays highlighting the specific parts you need to fix. AR achieves this by superimposing computer-generated images, sounds, and text onto the real world through smartphones, tablets, or specialized AR glasses. This technology offers a plethora of applications beyond entertainment. AR is transforming the retail industry by allowing customers to visualize products in their own spaces. It also empowers the service industry by providing technicians with real-time information and instructions while on-site. AR even aids in education, enabling students to interact with 3D models and explore complex concepts in an engaging way.
Mixed Reality (MR): Merging the Physical and Digital Realms
MR takes things a step further by creating a collaborative space where the real and virtual worlds coexist. Imagine a surgeon performing an operation with a real patient while simultaneously referencing a holographic 3D model of their anatomy projected onto the surgical field. MR headsets typically feature see-through displays that allow users to see the physical environment while simultaneously integrating virtual elements. This technology offers exciting possibilities for various fields. In design and architecture, MR allows professionals to visualize and interact with 3D models within their actual workspace. MR also holds immense potential for education and training, enabling students to learn complex procedures through interactive simulations that combine real-world tools with virtual elements.
The Future of XR: A World of Boundless Possibilities
As XR technologies continue to evolve and become more accessible, we can expect a future brimming with innovative applications. From revolutionizing remote collaboration to enhancing healthcare and education, XR holds the potential to transform the way we live, work, and learn. With its ability to create immersive and interactive experiences, XR is poised to become an integral part of our future.
Frequently Asked Questions for Extended Reality (XR)
Extended Reality (XR) is a broad term encompassing virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR). Here are some common questions and answers about XR:
General Questions
- What is extended reality (XR)?
- XR is a collective term for technologies that enhance the real world by overlaying or immersing users in digital information.
- What are the different types of XR?
- The three main types of XR are:
- Virtual Reality (VR): Creates a fully immersive digital environment, replacing the real world.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing it.
- Mixed Reality (MR): Combines elements of VR and AR, allowing users to interact with both real and virtual objects.
- The three main types of XR are:
- How is XR used?
- XR has a wide range of applications, including:
- Gaming and entertainment
- Education and training
- Healthcare
- Retail and marketing
- Architecture and design
- XR has a wide range of applications, including:
Technical Questions
- What hardware is needed for XR?
- XR typically requires specialized hardware, such as VR headsets, AR glasses, or MR devices.
- What software is used for XR applications?
- XR applications use various software platforms and development tools, depending on the specific XR technology and use case.
- What are the challenges of XR development?
- Challenges include:
- Hardware limitations
- User experience design
- Content creation
- Cost
- Challenges include:
Benefits and Future of XR
- What are the benefits of XR?
- XR can offer:
- Immersive experiences
- Enhanced learning and training
- Improved efficiency and productivity
- New opportunities for entertainment and social interaction
- XR can offer:
- What is the future of XR?
- The future of XR is promising, with continued advancements in technology and increasing adoption across various industries.

.jpg)