Africa: Shining Bright with Green Energy Potential
Across the vast landscapes of Africa, a new energy revolution is brewing. One that harnesses the abundant sunshine, whispering winds, and roaring rivers to power a brighter future.
Green energy, once a distant dream, is now becoming a tangible reality, promising to transform lives, economies, and the environment.
A Continent Blessed with Renewables:
Africa boasts a wealth of renewable energy resources that dwarf most other regions. Sun-drenched plains offer immense potential for solar power, with countries like South Africa leading the charge with massive solar farms. Gushing rivers like the Nile and Congo hold the key to hydropower, while the dramatic Great Rift Valley channels potent geothermal energy. Even the windswept coasts whisper promises of wind power generation.
Beyond Potential: Embracing the Change:
While the potential is undeniable, the journey towards widespread green energy adoption is underway. Countries are increasingly recognizing the benefits:
- Energy security and independence: Reliance on imported fossil fuels can be crippling. Renewables offer a path to self-sufficiency and energy security.
- Climate change mitigation: By reducing dependence on fossil fuels, Africa can play a crucial role in combating climate change, protecting its own vulnerable ecosystems and contributing to global efforts.
- Economic growth and job creation: The green energy sector is a burgeoning job market, attracting investment and creating opportunities for local communities.
- Improved health and well-being: Replacing polluting fossil fuels with clean energy sources leads to cleaner air and improved public health.
Challenges and the Road Ahead:
Despite the progress, challenges remain. Initial investment costs can be high, requiring innovative financing models and international collaboration. Grid infrastructure needs improvement to integrate more renewables effectively. Additionally, ensuring equitable access to energy in rural areas remains a critical concern.
A Future Powered by Green:
Despite the hurdles, the momentum is undeniable. From ambitious national targets to groundbreaking community-driven projects, Africa is embracing the green energy transition. With continued commitment, innovation, and international support, this continent has the potential to become a global leader in renewable energy, powering its own sustainable development and illuminating a brighter future for all.
Green Energy in Africa: Statistics Data
Green Energy in Africa: Statistics Painting a Promising Picture
Africa's vast potential for renewable energy is increasingly translating into tangible results, reflected in the growing statistics and data showcasing progress across the continent. Here's a snapshot of some key metrics:
Installed Capacity:
- Overall: As of 2022, Africa's total installed renewable energy capacity reached approximately 54 gigawatts (GW), nearly doubling since 2011. (Source: IRENA Renewable Energy Statistics 2022)
- Breakdown: Solar power leads the way with around 12.6 GW, followed by wind energy at 7.6 GW. Hydropower remains significant at 215 GW, but excludes pumped storage hydro for comparison. (Source: Statista - Renewable energy in Africa)
Generation:
- Renewable share: While variable depending on the region, the continent-wide average of electricity generation from renewable sources (excluding hydro) reached 8% in 2020. (Source: World Bank - Renewable energy consumption (% of total final energy consumption))
- Leading countries: Ethiopia stands out with 100% of its electricity generation coming from renewables, followed by Gabon (54%) and Kenya (79.7%). (Source: Research Spotlight: Renewable Energy in Africa - mo.ibrahim.foundation)
Investment:
- Annual average: Despite fluctuations, annual investments in renewable energy in Africa averaged around $9 billion between 2017 and 2021. (Source: REN21 Global Status Report 2023)
- Future projections: The World Bank estimates that Africa will require $300 billion in renewable energy investments by 2030 to achieve its climate goals. (Source: Green Energy in Africa: Financial Funds)
Impact:
- Job creation: The African Development Bank suggests transitioning to renewable energy could create up to 7 million jobs across the continent, boosting economic growth. (Source: Green Energy in Africa: Financial Funds)
- Health: Replacing polluting fossil fuels with clean energy sources leads to cleaner air and improved public health, particularly in urban areas.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While the data paints a promising picture, challenges remain, including:
- Unequal access: Rural areas often lack grid infrastructure, limiting access to renewable energy benefits.
- Financial constraints: Mobilizing sufficient capital for widespread adoption remains crucial.
- Policy and regulatory barriers: Streamlining regulations and incentivizing investment is essential.
Despite these challenges, the statistics highlight the significant progress and undeniable potential of green energy in Africa. With continued commitment, innovation, and addressing existing hurdles, Africa can harness its abundant renewable resources to power a sustainable and prosperous future.
Green Energy in Africa: Key Statistics Table
| Metric | Data | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Installed Capacity (2022) | 54 gigawatts (GW) | IRENA Renewable Energy Statistics 2022 |
| Breakdown: | ||
| - Solar Power | 12.6 GW | Statista - Renewable energy in Africa |
| - Wind Energy | 7.6 GW | Statista - Renewable energy in Africa |
| - Hydropower (excluding pumped storage) | 215 GW | Statista - Renewable energy in Africa |
| Renewable Electricity Generation (excluding hydro, 2020) | 8% | World Bank - Renewable energy consumption (% of total final energy consumption) |
| Leading Countries in Renewable Generation: | ||
| - Ethiopia | 100% | Research Spotlight: Renewable Energy in Africa - mo.ibrahim.foundation |
| - Gabon | 54% | Research Spotlight: Renewable Energy in Africa - mo.ibrahim.foundation |
| - Kenya | 79.7% | Research Spotlight: Renewable Energy in Africa - mo.ibrahim.foundation |
| Average Annual Investment (2017-2021) | $9 billion | REN21 Global Status Report 2023 |
| Estimated Investment Needed by 2030 | $300 billion | Green Energy in Africa: Financial Funds |
| Potential Job Creation | Up to 7 million | African Development Bank |
Note: This table includes only a selection of key statistics. Additional data can be added based on your specific interests.
Successful green energy projects in Africa
Green Energy Success Stories in Africa: Beacons of a Brighter Future
Across Africa, the abundant potential for renewable energy is translating into tangible results through numerous successful projects. These initiatives not only deliver clean, reliable power but also create jobs, improve lives, and serve as models for future development. Here are some shining examples:
Morocco's Noor Ouarzazate Solar Complex: Nicknamed "The Moroccan Sun," this concentrated solar power (CSP) plant reigns as the world's largest, spanning an impressive 3,000 hectares in the Sahara Desert. Five individual plants utilize diverse CSP technologies to generate a combined 580 MW of clean electricity, powering over 1 million homes.
South Africa's Lesedi Photovoltaic Plant: Near Kimberley, this massive solar farm boasts a peak capacity of 100 MW, ranking among Africa's largest. It provides clean energy to over 80,000 households and created over 1,000 jobs during construction and operation.
Kenya's Lake Turkana Wind Power Project: Situated in remote northern Kenya, this wind farm stands as the largest in East and Central Africa with a capacity of 310 MW. It supplies clean energy to over 1.5 million Kenyans and significantly reduced the country's dependence on expensive diesel-generated power.
Rwanda's Off-Grid Solar Revolution: Rwanda has made impressive strides in providing off-grid solar solutions to rural communities. Through various initiatives, over 2 million Rwandans now have access to clean and affordable electricity, empowering homes, businesses, and healthcare facilities.
Ethiopia's Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD): While facing complexities, the GERD is a massive hydroelectric project on the Blue Nile with a planned capacity of 6,000 MW. Upon completion, it will be Africa's largest hydropower plant and is expected to provide clean energy to Ethiopia and neighboring countries.
Expanding the Horizon:
- Egypt's Benban Solar Park: With a capacity of 1.65 GW, this colossal park is Africa's largest and ranks among the world's biggest. It helps reduce Egypt's reliance on expensive fossil fuels and paves the way for a renewable energy transition.
- Ghana's Floating Solar Power Plant: This innovative project on the Volta Lake, West Africa's first floating solar installation, boasts a 250 MW capacity. It helps alleviate Ghana's power shortages and showcases the potential for similar projects in other nations.
- Namibia's Green Hydrogen Project: Namibia is building a facility to produce green hydrogen, derived from renewable energy. This project has the potential to make Namibia a global leader in clean hydrogen production and contribute to decarbonizing the global economy.
These projects are just a glimpse into the numerous successful initiatives driving Africa's clean energy transition. They stand as testaments to the continent's commitment to a sustainable future and offer valuable lessons and inspiration for further development. By harnessing its abundant renewable resources and fostering innovation, Africa is poised to become a global leader in the green energy revolution, ensuring a brighter future for its people and the planet.
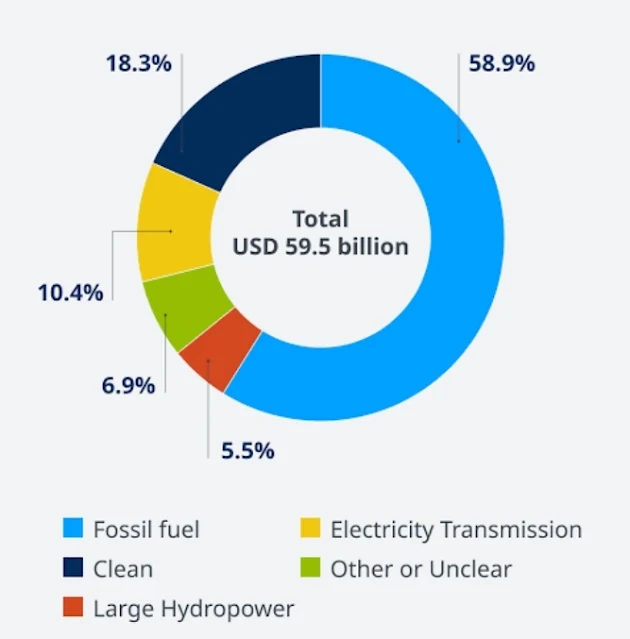
Green Energy in Africa: Financial Funds
Green Energy in Africa: Financial Funds Fueling a Sustainable Future
Africa's vast potential for renewable energy is attracting significant financial support from a diverse range of sources. These funds are playing a crucial role in accelerating the continent's green energy transition, unlocking investments, and driving innovation. Here's a closer look at some key players:
Public Funds:
- Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs): The World Bank, African Development Bank (AfDB), and others offer concessional loans, grants, and technical assistance to support renewable energy projects. For example, the AfDB's Sustainable Energy Fund for Africa (SEFA) provides catalytic finance to de-risk investments and attract private capital.
- National Development Banks: Development finance institutions within African countries play a critical role in mobilizing domestic resources and channelling them towards green energy projects.
- Climate Funds: Dedicated climate funds like the Green Climate Fund (GCF) and the Global Environment Facility (GEF) provide grants and concessional loans to support climate-friendly initiatives, including renewable energy projects in Africa.
Private Equity Funds:
- Dedicated Green Energy Funds: Several private equity funds specifically focus on investing in renewable energy projects across Africa. These funds typically target larger-scale projects with established track records and offer patient capital, allowing for longer project development cycles.
- Impact Investment Funds: Some impact investors include renewable energy within their broader portfolios, seeking positive social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. These funds can play a crucial role in supporting smaller, innovative projects or those in challenging environments.
- Infrastructure Funds: Infrastructure funds are increasingly looking to invest in renewable energy projects due to their attractive risk-return profiles and long-term stability.
Innovative Financing Mechanisms:
- Green Bonds: African countries are issuing green bonds to raise capital for specific green energy projects, attracting investors seeking sustainable investments.
- Carbon Offsets: Projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions can generate carbon credits, which can be sold to companies seeking to offset their emissions, providing additional revenue streams for renewable energy projects.
- Blending Finance: Blending public and private funds can reduce the financial risk for private investors and make renewable energy projects more attractive, leveraging the strengths of both sources.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite the growing availability of funds, some challenges remain:
- Lack of Access to Finance: Smaller developers and projects in rural areas often struggle to access funding.
- Local Currency Financing: Limited availability of local currency financing can create currency exchange risks for projects.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Uncertain regulatory frameworks can discourage investment.
However, opportunities abound:
- Technological Advancements: Falling costs of renewable technologies and innovative solutions are making projects more affordable and attractive.
- Growing Interest: Increasing investor interest in sustainable investments creates a favorable environment for green energy projects in Africa.
- Policy Support: Supportive government policies and regulations can further attract investment and accelerate the transition.
Financial funds are playing a critical role in unlocking Africa's green energy potential. By diversifying funding sources, addressing challenges, and seizing opportunities, Africa can continue to leverage its abundant renewable resources to build a sustainable and prosperous future.
Green Energy in Africa: New Technology
Green Energy in Africa: A Landscape Bursting with New Technology
Across Africa, a wave of innovative technologies is transforming the green energy landscape. These advancements, coupled with the continent's abundant renewable resources, are paving the way for a sustainable and electrifying future. Let's explore some of the most exciting developments:
Solar Power Innovations:
- Miniaturization: Portable and foldable solar panels are empowering rural communities with off-grid electricity, reaching areas where traditional grid infrastructure is lacking.
- Organic Photovoltaics (OPVs): These lightweight, flexible solar cells can be integrated into diverse surfaces, from clothing to building materials, creating opportunities for distributed generation.
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) advancements: New designs and materials are boosting the efficiency and affordability of CSP plants, making them more competitive with traditional energy sources.
Wind Power on the Rise:
- Small wind turbines: Compact and adaptable turbines are bringing wind power to urban areas and remote locations, complementing larger-scale wind farms.
- Vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWTs): These innovative designs are less susceptible to wind direction and turbulence, making them suitable for complex terrains and urban environments.
- Hybrid wind-solar systems: Combining these technologies optimizes energy capture and utilization, ensuring a more reliable and consistent power supply.
Hydropower with a Twist:
- Run-of-the-river hydro: These smalletyr-scale hydro projects minimize environmental impact and are well-suited for rural areas with flowing rivers.
- Pumped hydro storage: Storing excess renewable energy by pumping water uphill and releasing it through turbines generates electricity when needed, improving grid stability and integrating intermittent renewables.
- Tidal and wave energy technologies: Despite being in their early stages, these innovations harness the power of ocean currents and waves, offering vast potential for coastal regions.
Beyond Generation:
- Battery storage technologies: Advancements in lithium-ion and other battery technologies are crucial for storing renewable energy and ensuring grid stability, addressing the intermittency challenge.
- Smart grids: Utilizing digital technologies and AI, smart grids optimize energy distribution, reduce losses, and integrate diverse renewable sources seamlessly.
- Blockchain for renewables: This technology can enhance transparency, traceability, and financing for renewable energy projects, boosting investor confidence and efficiency.
Challenges and the Road Ahead:
While these technologies hold immense promise, challenges remain:
- Cost reduction: Making some new technologies more cost-effective requires further research and development.
- Infrastructure development: Expanding and upgrading transmission and distribution grids is crucial for wider integration of renewables.
- Capacity building: Skilled personnel are needed to install, operate, and maintain these innovative systems.
Looking Forward:
Despite the hurdles, Africa's commitment to green energy, combined with the rapid evolution of new technologies, paints a bright picture. By embracing innovation, overcoming challenges, and fostering collaboration, Africa can harness its renewable potential to power a sustainable and prosperous future for its people and the planet.