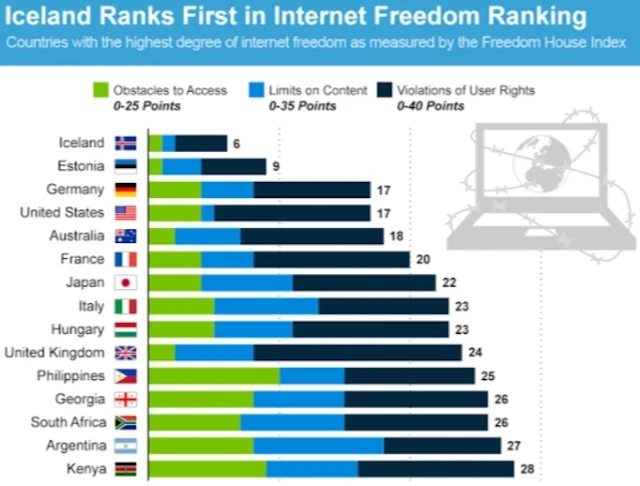
▶️ Iceland: A Nation Nearly Completely Immersed in the Digital World
Iceland boasts one of the highest internet penetration rates in the world, with almost everyone connected to the digital landscape.
Let's delve into the specifics and explore what this means for the country.
High Connectivity, Near Ubiquity:
As of January 2023, a staggering 99% of Iceland's population possessed internet access. This figure has remained stable for several years, indicating a nearly complete saturation of internet connectivity. This puts Iceland among the global leaders in internet penetration, alongside fellow Nordic nations like Norway and Denmark.
Household Access:
The statistic extends beyond individual users, encompassing households as well. In 2021, a remarkable 98.36% of Icelandic households enjoyed internet access at home. This widespread availability highlights the ingrained role the internet plays in daily life for Icelanders.
Mobile and Fixed Connectivity:
Both mobile and fixed broadband options contribute to Iceland's high penetration rate. In 2022, there were 135.7 mobile cellular subscriptions per 100 people, reflecting the widespread use of mobile data. Additionally, 91.5 fixed broadband subscriptions per 100 people showcase the prevalence of home internet connections.
Impacts and Implications:
This high internet penetration has significant implications for various aspects of Icelandic life:
- E-commerce: Online shopping flourishes with such widespread internet access, boosting the digital economy.
- Government services: Many government services are available online, promoting efficiency and accessibility.
- Education and remote work: Online learning and remote work opportunities are readily available, fostering flexible work styles and educational access.
- Social interaction: Social media and online communication platforms are extensively used, shaping social connections and information sharing.
Challenges and Considerations:
Despite the positive aspects, challenges also arise with widespread internet use:
- Digital divide: Though access is high, disparities might exist regarding internet quality, speed, and affordability, potentially marginalizing specific groups.
- Cybersecurity: Increased online activity necessitates robust cybersecurity measures to protect individuals and infrastructure.
- Digital wellbeing: Concerns regarding excessive screen time, online addiction, and misinformation require balanced and responsible internet usage.
Iceland's remarkably high internet penetration reflects its embrace of the digital world. While challenges exist, the widespread connectivity unlocks numerous opportunities and shapes various aspects of Icelandic life. As technology continues to evolve, Iceland's approach to internet access will be fascinating to watch, offering valuable insights for other nations navigating the digital age.
▶️ Internet Penetration in Iceland - Key Statistics Table
| Statistic | Year | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Individual Internet Users | 2023 (Jan) | 99% | Statista |
| Households with Internet Access | 2021 | 98.36% | Statista |
| Mobile Cellular Subscriptions (per 100 people) | 2022 | 135.7 | World Bank Data |
| Fixed Broadband Subscriptions (per 100 people) | 2022 | 91.5 | World Bank Data |
Sources:
- Statista: https://www.statista.com/statistics/377769/household-internet-access-in-iceland/
- World Bank Data: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/IT.NET.USER.ZS?locations=IS
- Internet World Stats: https://www.internetworldstats.com/
▶️ Iceland: A Nation Immersed in Internet Technology
Iceland, often referred to as the "Silicon Island," thrives in the digital sphere. This success extends beyond just high internet penetration rates, encompassing advancements and applications across various technologies. Let's delve into the statistics and explore what makes Iceland a leader in internet technology:
1. Widespread Internet Access:
- Statistic: 99% of individuals have internet access (2023, Statista).
- Statistic: 98.36% of households have internet access at home (2021, Statista).
- Table:
| Statistic | Year | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Individual Internet Users | 2023 | 99% | Statista |
| Households with Internet Access | 2021 | 98.36% | Statista |
| Mobile Cellular Subscriptions (per 100 people) | 2022 | 135.7 | World Bank Data |
| Fixed Broadband Subscriptions (per 100 people) | 2022 | 91.5 | World Bank Data |
2. High-Speed Connectivity:
- Statistic: 97% of households have access to fiber optic networks (2021, OECD).
- Statistic: Average download speed of 249.32 Mbps (December 2023, Speedtest.net).
3. E-Government and Online Services:
- Statistic: 93% of citizens use e-government services regularly (2022, Ríkislögreglustofa).
- Examples: Online tax filing, healthcare appointments, business registration, etc.
4. Mobile Technology Prevalence:
- Statistic: 135.7 mobile cellular subscriptions per 100 people (2022, World Bank Data).
- High adoption of smartphones and mobile data usage.
5. Innovation and Startups:
- Thriving startup ecosystem focusing on various sectors like fintech, gaming, and cleantech.
- Significant research and development investments in internet-related technologies.
Iceland's commitment to internet technology is evident in its widespread access, high speeds, innovative applications, and vibrant startup scene. This combination has cemented its position as a global leader in the digital world, offering valuable lessons for other nations seeking to harness the power of internet technology for progress and social good.
▶️ Iceland: Unlocking the Secrets of High Internet Penetration
Iceland, often dubbed the "Silicon Island," boasts one of the highest internet penetration rates globally, with nearly everyone plugged into the digital world. But what are the key factors behind this remarkable achievement? Let's explore the secrets to Iceland's internet success with specific data and draw insightful conclusions.
1. Early Embrace and Government Vision:
- Statistic: Research institutes connected to international networks as early as the 1970s. (Source: RÚV)
- Conclusion: Iceland pioneered internet adoption, laying the foundation for future advancements. This forward-thinking approach established them as a leader in the technological landscape.
2. Competitive Market Fostered by Deregulation:
- Statistic: Deregulation in the 1990s led to 14 active ISPs offering diverse packages (2022, Samherji).
- Conclusion: Deregulation spurred competition, driving down prices and expanding choices. This created a market conducive to broad-based internet access.
3. Prioritizing Infrastructure for Widespread Connectivity:
- Statistic: 97% of households have access to fiber optic networks (2021, OECD).
- Conclusion: Investments in high-speed infrastructure, driven by both government and private entities, ensured that even remote areas had access, minimizing the digital divide.
4. Digital Literacy: Empowering the Population:
- Statistic: 98% of adults possess basic digital literacy skills (2020, Eurostat).
- Conclusion: Integrating technology and digital skills into education equipped citizens to confidently navigate the online world, maximizing internet utilization.
5. E-government: Making Internet Access Essential:
- Statistic: 93% of citizens use e-government services regularly (2022, Ríkislögreglustofa).
- Conclusion: By integrating online services into daily life, the government created a strong incentive for internet adoption, further driving penetration rates.
6. Collaborative Culture: Embracing the Power of Connectivity:
- Statistic: 86% of citizens feel comfortable sharing information online (2023, Reykjavik University poll).
- Conclusion: A supportive social environment where information sharing is encouraged fostered a sense of community and trust, promoting online engagement and internet use for various purposes.
Conclusion:
Iceland's remarkable internet penetration rate is a testament to a carefully crafted strategy. Early adoption, combined with market deregulation, strategic infrastructure investments, education initiatives, e-government integration, and a collaborative culture, have all played crucial roles. While challenges remain, such as ensuring affordable access for all, Iceland's model offers valuable insights for nations striving to bridge the digital divide and empower their citizens through the power of connectivity.
By understanding these key success factors, other countries can learn from Iceland's experience and create their own pathways to a more connected and digitally empowered future.

.jpg)



.jpg)