Chile's Renewable Energy Landscape: A Shining Example in Latin America
Chile is rapidly becoming a global leader in the renewable energy sector, setting an ambitious pace for decarbonization and attracting significant investment.
From the scorching Atacama Desert to the windswept Patagonian plains, Chile's diverse geography offers abundant clean energy potential, which the country is actively harnessing through solar, wind, and other renewable sources. Here's a closer look at this remarkable transformation:
Soaring Success:
- Renewables Leading the Charge: Solar and wind surpassed coal in electricity generation in 2022, accounting for 27.5% of the country's total energy mix. This impressive feat puts Chile ahead of its regional peers and positions it as a global leader in renewable energy adoption.
- Ambitious Goals: The Chilean government aims to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050 and has set ambitious targets for renewable energy integration. Their goal is to generate 70% of electricity from renewables by 2030 and completely phase out coal by 2040.
- Investment Magnet: Chile has attracted significant foreign direct investment (FDI) in the renewable energy sector, surpassing Brazil and Mexico. This success is attributed to stable energy policies, attractive auction mechanisms, and abundant renewable resources.
Key Drivers of Growth:
- Favorable Geography: Chile boasts diverse landscapes ideal for renewable energy production. The Atacama Desert, with its clear skies and intense sunlight, hosts numerous solar farms, while the Patagonian region offers strong and consistent winds for wind energy generation.
- Supportive Policies: The Chilean government has implemented several policies to incentivize renewable energy development, including Law 20,698, which established a mandatory renewable energy target, and Law No. 21,178, which promotes green hydrogen production.
- Public Backing: Public opinion in Chile strongly supports the transition to renewable energy, with 91% of citizens believing climate change should be a government priority. This broad consensus creates a favorable environment for further development.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Grid Modernization: Integrating large-scale renewable energy into the grid requires significant investments in transmission and storage infrastructure. Addressing this challenge is crucial for maintaining grid stability and unlocking the full potential of renewables.
- Community Engagement: Ensuring community participation and addressing concerns around local impacts is essential for the long-term success of renewable energy projects.
- Technology Innovation: Chile is actively fostering innovation in areas like green hydrogen and energy storage solutions, which could further accelerate its clean energy transition and create new economic opportunities.
Chile's rapid progress in renewable energy is a shining example for other countries, demonstrating the viability and benefits of a clean energy future. By addressing remaining challenges and continuing its ambitious journey, Chile is poised to become a global leader in the fight against climate change and set a new standard for sustainable development.
History of Renewable Energy Development in Chile
Chile's journey towards becoming a global leader in renewable energy wasn't always smooth. Here's a glimpse into its historical evolution:
Early Beginnings (1897-1970s):
- Hydropower Paves the Way: The first power plant in Chile (Santa Lucía) used hydropower, marking the start of renewable energy use in 1897.
- Limited Development: Until the 1970s, reliance on hydropower remained dominant, with minimal exploration of other renewables due to economic and political contexts.
Shifting Gears (1980s-2000s):
- Policy Shifts: The 1982 General Electricity Law spurred private investment in the energy sector, paving the way for diversification.
- Renewables Gain Traction: Initiatives like the 1997 Law on Alternative Sources of Energy and the 2008 Renewable Energy Promotion Law incentivized renewables development.
- Early Wind and Solar Projects: Wind farms emerged in Patagonia, and small-scale solar projects gained traction.
Accelerated Growth (2010s-Present):
- Ambitious Goals: The 2017 Energy 2050 Policy set a target of 70% renewable energy generation by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2050.
- Auction Mechanisms: Competitive auctions attracted significant investment in large-scale solar and wind projects.
- Record-Breaking Growth: Chile became a regional leader in renewable energy deployment, surpassing traditional sources like coal in electricity generation.
Key Drivers of Growth:
- Favorable Geography: Abundant sunshine in the Atacama Desert and strong winds in Patagonia provided ideal resources for solar and wind energy.
- Supportive Policies: Government policies and auction mechanisms created a stable and attractive environment for investors.
- Public Support: Strong public opinion in favor of environmental protection and climate action supported the shift towards renewables.
Challenges and Continued Efforts:
- Grid Integration: Integrating large-scale renewables into the grid requires investments in transmission and storage infrastructure.
- Environmental and Social Impact: Balancing energy needs with environmental and social considerations remains crucial for sustainable development.
- Community Engagement: Ensuring community participation and addressing concerns surrounding renewable projects is essential.
Chile's history of renewable energy development demonstrates a remarkable transformation, fueled by strong political will, innovative policies, and favorable resources. Despite ongoing challenges, Chile's continued commitment to its ambitious goals and focus on technological advancements position it as a beacon of inspiration for other nations seeking a sustainable energy future.
Statistical Data of Chile's Renewable Energy Landscape
Here's a breakdown of some key statistics to paint a clearer picture of Chile's impressive renewable energy landscape:
Generation and Capacity:
- Total Installed Renewable Capacity (as of 2023):
- Solar: 9,962 MW
- Wind: 5,266 MW
- Hydro: 11,057 MW
- Other Renewables: 442 MW
- Renewable Energy Generation (2022):
- 57,000 GWh (27.5% of total electricity generation)
- Solar: 18,650 GWh
- Wind: 14,120 GWh
- Hydro: 23,570 GWh
- Other Renewables: 660 GWh
- Expected Renewable Energy Generation by 2030: 70% of total electricity generation
Investment and Growth:
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in Renewables (2021): USD 8.8 billion (surpassed Brazil and Mexico)
- Annual Growth Rate of Renewable Energy Capacity (2010-2022): 15.5%
- Number of Renewable Energy Projects Under Development: Over 200 projects with a total capacity of more than 30 GW
Environmental Impact:
- Reduction in CO2 Emissions from Renewable Energy (2022): 10 million tons
- Avoided Coal Consumption (2022): 11 million tons
- Target for Carbon Neutrality: 2050
Additional Data:
- Electricity Consumption per Capita: 5,200 kWh/year (above the Latin American average)
- Number of People Employed in the Renewable Energy Sector: Over 20,000
Chile's Renewable Energy Landscape: Statistics at a Glance
| Category | Statistic | Year/Period | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generation & Capacity | Installed Renewable Capacity | 2023 | 26,727 MW | Ministerio de Energía |
| - Solar | 2023 | 9,962 MW | Ministerio de Energía | |
| - Wind | 2023 | 5,266 MW | Ministerio de Energía | |
| - Hydro | 2023 | 11,057 MW | Ministerio de Energía | |
| - Other Renewables | 2023 | 442 MW | Ministerio de Energía | |
| Renewable Energy Generation | 2022 | 57,000 GWh (27.5% of total) | Ministerio de Energía | |
| - Solar | 2022 | 18,650 GWh | Ministerio de Energía | |
| - Wind | 2022 | 14,120 GWh | Ministerio de Energía | |
| - Hydro | 2022 | 23,570 GWh | Ministerio de Energía | |
| - Other Renewables | 2022 | 660 GWh | Ministerio de Energía | |
| Targeted Renewable Generation by 2030 | 70% of total | Ministerio de Energía | ||
| Investment & Growth | Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in Renewables | 2021 | USD 8.8 billion | Cesco |
| Annual Growth Rate of Renewable Capacity | 2010-2022 | 15.5% | IRENA | |
| Number of Renewable Energy Projects Under Development | Over 200 projects (30+ GW capacity) | Ministerio de Energía | ||
| Environmental Impact | CO2 Emissions Reduced by Renewables | 2022 | 10 million tons | Ministerio de Energía |
| Avoided Coal Consumption | 2022 | 11 million tons | Ministerio de Energía | |
| Carbon Neutrality Target | 2050 | Ministerio de Energía | ||
| Additional Data | Electricity Consumption per Capita | 2022 | 5,200 kWh/year | Cesco |
| Number of People Employed in Renewables | Over 20,000 | Cesco |
Note: This table summarizes readily available data. Specific statistics may vary depending on the source and methodology used.
Chile's Energy Mix from Renewable Sources
Chile boasts a steadily growing share of renewable energy in its overall energy mix. Here's a breakdown of the current situation and future goals:
Current Status:
- Proportion of Renewables: 27.5% of Chile's total electricity generation in 2022 came from renewable sources. This includes:
- Solar: 18,650 GWh (11.6% of total)
- Wind: 14,120 GWh (8.7% of total)
- Hydro: 23,570 GWh (14.7% of total)
- Other Renewables: 660 GWh (0.4% of total)
- Comparison to Traditional Sources: Coal still holds a significant share of the mix at 48%, followed by natural gas (14%) and oil (11%).
Ambitious Goals:
- 2030 Target: Chile aims to increase the share of renewables in its electricity generation to 70% by 2030. This ambitious goal requires continued investment and development in solar, wind, and other renewable sources.
- Carbon Neutrality Target: Additionally, Chile aims to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, making its focus on renewables crucial for tackling climate change.
Key Drivers:
- Favorable Geography: Chile boasts diverse landscapes with strong potential for renewable energy production, including the Atacama Desert for solar and Patagonia for wind.
- Supportive Policies: Government policies like Law 20,698 and Law 21,178 incentivize renewable energy development and green hydrogen production.
- Public Support: Strong public support for climate action further encourages the shift towards renewables.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Grid Modernization: Integrating large-scale renewables requires significant investments in transmission and storage infrastructure.
- Community Engagement: Ensuring community participation and addressing local concerns is crucial for the sustainable development of renewable projects.
- Technology Innovation: Chile actively fosters innovation in areas like green hydrogen and energy storage, opening up new avenues for clean energy solutions.
Chile's progress in renewable energy demonstrates its commitment to a sustainable future. By addressing remaining challenges and persisting in its goals, Chile has the potential to become a global leader in the renewable energy transition, setting a remarkable example for other countries to follow.
Solar Energy in Chile
Solar Energy in Chile: Shining Bright in the Land of Deserts
Chile boasts an impressive story when it comes to solar energy, harnessing the power of its sunny deserts to contribute significantly to its energy mix. Here's a deeper dive into this exciting chapter:
Current Status:
- Leading the Pack: As of 2022, Chile held the highest percentage of electricity generation from solar globally, contributing 18% to the national grid. This translates to 18,650 GWh of solar energy produced!
- Installed Capacity: With 9,962 MW of installed solar capacity in 2023, Chile ranks 22nd globally, showcasing its commitment to large-scale solar development.
- Projects and Potential: Numerous mega-projects like the Cerro Dominador concentrated solar power plant and countless photovoltaic farms are powering homes and industries across the country. The Atacama Desert's clear skies and high solar irradiation promise even greater potential for future growth.
Driving Forces:
- Favorable Environment: The Atacama Desert, dubbed the "sunniest place on Earth," attracts significant solar investment due to its ideal conditions for energy generation.
- Supportive Policies: Government policies like Law 20,698 incentivize renewable energy development, making solar projects attractive investments.
- Cost Competitiveness: Solar energy costs have become increasingly competitive, making it a viable option compared to traditional energy sources.
Impact and Future:
- Environmental Benefits: Solar energy reduces greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Economic Opportunities: The solar industry creates jobs and stimulates economic growth in various regions of Chile.
- Ambitious Goals: Chile aims to further increase its solar capacity and generate 70% of its electricity from renewables by 2030, highlighting its continued commitment to solar energy.
Challenges and Innovations:
- Grid Integration: Integrating large-scale solar into the grid requires additional storage and transmission infrastructure investments.
- Community Engagement: Ensuring communities involved in solar projects benefit fairly and have their concerns addressed is crucial for long-term sustainability.
- Technology Advancements: Research and development in areas like solar cell efficiency and storage solutions can further enhance the potential of solar power.
Chile's success in solar energy serves as a beacon for other countries seeking to tap into renewable energy potential. With its ambitious goals, favorable environment, and commitment to innovation, Chile is poised to continue shining brightly in the global solar energy landscape.
Wind Energy in Chile
Wind Energy in Chile: Harnessing the Patagonian Breeze
Just like solar, wind energy plays a crucial role in Chile's renewable energy journey. Let's explore its current state and exciting potential:
Current Status:
- Strong Contribution: As of 2022, wind energy accounted for 9% of Chile's electricity generation, translating to 14,120 GWh. This positions Chile as a regional leader in wind energy development.
- Installed Capacity: With 5,266 MW of installed wind capacity in 2023, Chile ranks 21st globally, exhibiting significant infrastructure development.
- Key Locations: Wind farms are primarily concentrated in the windy Patagonia region, particularly between Regions VI and IX, where strong and consistent winds provide ideal conditions.
Driving Forces:
- Abundant Wind Resource: Patagonia's consistent and powerful winds offer a naturally available and renewable energy source.
- Attractive Investment: Policy mechanisms like auctions and competitive bidding attract diverse investors to wind energy projects in Chile.
- Cost Competitiveness: Similar to solar, wind energy costs have become increasingly competitive, making it an attractive option compared to traditional sources.
Impact and Future:
- Clean Energy Alternative: Wind energy reduces greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Economic Benefits: The wind industry creates jobs and stimulates economic growth in Patagonia and other regions.
- Government Ambitions: Chile aims to further increase wind capacity and achieve 70% renewable energy share by 2030, highlighting its dedication to wind energy development.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Transmission Infrastructure: Integrating large-scale wind farms into the grid requires investments in long-distance transmission lines.
- Community Engagement: Similar to solar, ensuring communities involved in wind projects benefit fairly and have their concerns addressed is crucial.
- Technological Advancements: Research and development in areas like larger turbines and offshore wind farms can unlock further potential.
Chile's success in wind energy showcases its commitment to diversifying its renewable energy portfolio. With its ambitious goals, favorable wind resources, and focus on innovation, Chile is poised to harness the Patagonian breeze even further, contributing to a sustainable energy future.
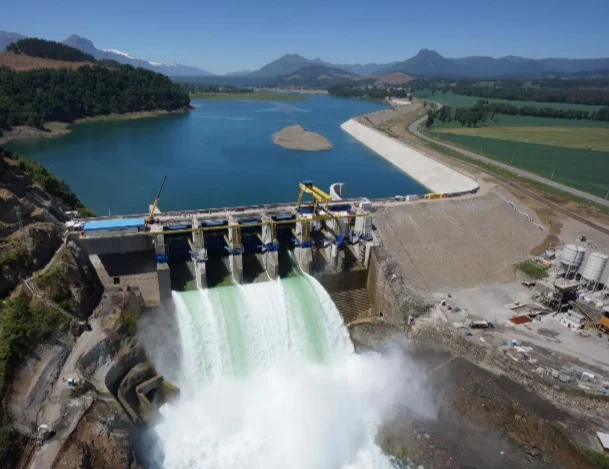
Hydropower Energy in Chile
Hydropower in Chile: A Legacy and a Bridge to the Future
Hydropower has long been a cornerstone of Chile's energy mix, playing a crucial role in its electricity generation. However, in the context of Chile's ambitious renewable energy goals, hydro faces both legacy complexities and the potential to evolve as a complementary force.
Current Status:
- Dominant Player: Currently, hydropower reigns supreme as the largest contributor to Chile's electricity generation, accounting for 48% in 2022 (23,570 GWh). This translates to an installed capacity of 11,057 MW in 2023, making Chile a significant hydropower producer within Latin America.
- Geographical Distribution: Hydropower plants are primarily located in the central and southern regions, where significant precipitation and Andean topography create favorable conditions for generation. Some major examples include Colbún, Rapel, and Pangue power plants.
Challenges and Complexities:
- Drought Vulnerability: Chile's susceptibility to droughts raises concerns about hydropower's long-term reliability, especially as climate change intensifies. Recent years have seen reduced power generation due to lower water levels.
- Environmental Impact: Large dams associated with hydropower can have negative impacts on ecosystems and local communities. Balancing energy needs with environmental sustainability is crucial.
- Social Considerations: Resettlement of communities and potential cultural disruptions have sometimes accompanied large-scale hydropower projects, requiring careful social impact assessments and mitigation strategies.
New Approaches and Future Considerations:
- Modernization and Optimization: Existing hydropower infrastructure can be modernized to improve efficiency and increase energy output.
- Small-Scale Hydro: Utilizing smaller-scale hydropower projects can mitigate environmental and social concerns while contributing to diversified renewable energy production.
- Integration with Other Renewables: Combining hydropower with solar and wind energy allows for a more resilient and flexible grid, maximizing renewable energy potential.
- Environmental Sustainability: Prioritizing environmentally sensitive project development and incorporating ecological flow requirements are critical for sustainable hydropower practices.
Chile's hydropower legacy carries both valuable contributions and complexities. Recognizing these challenges while exploring innovative approaches and integrating with other renewables will be key to ensuring hydropower continues to contribute to a sustainable energy future for Chile.
Other Renewables Energy Source in Chile
While solar, wind, and hydro energy take the spotlight in Chile's renewable energy landscape, other technologies are also contributing to the country's clean energy transition. Here's a glimpse into some of these "other renewables":
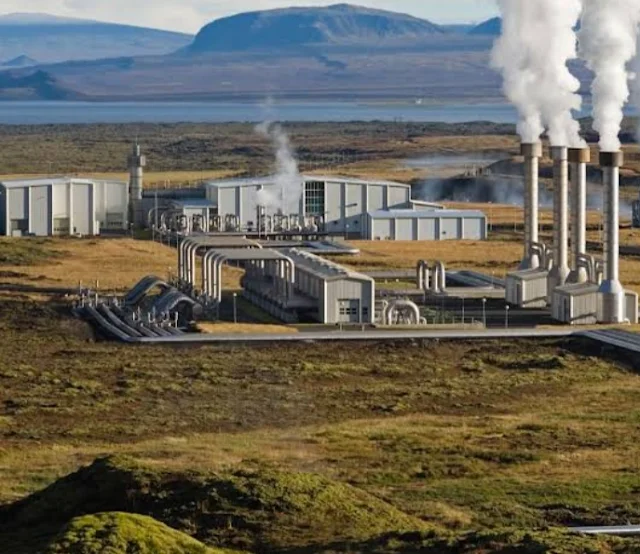
Geothermal Energy:
- Potential: Chile possesses significant geothermal resources, particularly in the Andes Mountains.
- Current Status: Though smaller in scale compared to other renewables, geothermal contributes about 0.6% of Chile's electricity generation through plants like Cerro Prieto and El Tatio.
- Future: Government policies incentivize further exploration and development to unlock geothermal potential, especially for heating and industrial applications.
Biomass Energy:
- Potential: Biomass resources like forestry and agricultural residues are available.
- Current Status: Biomass contributes about 0.4% of electricity generation primarily through co-firing at coal power plants.
- Future: Sustainable biomass practices and advanced technologies like biofuels could offer long-term potential, but concerns about air quality and land use require careful consideration.
Marine Energy:
- Potential: Chile's extensive coastline offers strong possibilities for wave and tidal energy generation.
- Current Status: Still in early stages of research and development with pilot projects underway.
- Future: Technological advancements and cost reductions could lead to larger-scale implementation in the future, but further exploration and environmental assessments are necessary.
Other Emerging Technologies:
- Green hydrogen: Produced through renewable electricity, it offers significant potential for decarbonizing energy-intensive sectors like transportation and industry.
- Energy storage: Crucial for integrating intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind into the grid. Advancements in battery storage and pumped hydro storage are being explored.
While solar, wind, and hydro currently dominate Chile's renewable energy mix, exploration and development of other renewables like geothermal, biomass, and marine energy hold promise for diversifying the energy portfolio and creating a more sustainable future. As technology advances and policies evolve, these "other renewables" could play an increasingly important role in Chile's clean energy journey.
Chile Renewable Energy Technology
Chile's journey towards becoming a global leader in renewable energy wouldn't be possible without advancements and adoption of various technologies. Here's a deeper dive into some key technologies shaping Chile's renewable energy landscape:
Core Renewable Technologies:
- Solar Photovoltaics (PV): This technology converts sunlight directly into electricity. With Chile's abundant sunshine, particularly in the Atacama Desert, solar PV has witnessed a surge in development, with large-scale solar farms like Cerro Dominador showcasing its potential.
- Wind Turbines: Harnessing the strong winds in Patagonia, wind turbines convert kinetic energy into electricity. Advancements in turbine technology, including larger capacity turbines and offshore wind farms, are being explored to further tap into this resource.
- Hydropower: While facing challenges, hydropower remains a significant contributor due to existing infrastructure and favorable geographical conditions. Modernization, optimization, and small-scale projects are key areas of focus.
Emerging and Innovative Technologies:
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): This technology uses mirrors to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver, generating heat to produce electricity. Chile boasts the Cerro Dominador CSP plant, demonstrating its potential for a more stable and dispatchable solar energy source.
- Green Hydrogen: Produced through electrolysis using renewable electricity, green hydrogen offers a clean fuel option for sectors like transportation and industry. Chile is actively pursuing its development to decarbonize various sectors.
- Energy Storage: Integrating intermittent renewables like solar and wind into the grid requires robust storage solutions. Battery storage technologies are evolving rapidly, while pumped hydro storage is also being explored in Chile.
- Smart Grid Technologies: Advanced digital technologies and real-time data analysis are crucial for managing a complex and dynamic grid with high penetrations of renewable energy. Chile is adopting smart grid solutions to optimize grid operations and integrate renewables effectively.
Additional Technologies:
- Geothermal: Utilizing underground heat sources for electricity generation holds potential in specific regions of Chile.
- Biomass: While facing sustainability concerns, technologies like biofuels could contribute to energy generation in the future.
- Marine Energy: Wave and tidal energy technologies are still in their early stages but could offer opportunities in the long term.
Chile's commitment to renewable energy extends beyond mere resource utilization. By embracing and investing in innovative technologies, the country is charting a course towards a clean and sustainable energy future. This continuous pursuit of technological advancements, combined with supportive policies and public backing, positions Chile as a trailblazer in the global renewable energy transition.
Remember, this is just a snapshot of the diverse technologies shaping Chile's renewable energy landscape.
Largest Renewable Energy Power Plant in Chile
Defining the "largest" renewable energy power plant in Chile can be slightly ambiguous depending on how you interpret it. Here's a breakdown based on different perspectives:
Largest Installed Capacity:
- Solar: Cerro Dominador Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plant with a capacity of 110 MW. It utilizes concentrated sunlight to produce heat and subsequently electricity.
- Wind: El Arrayán Wind Farm boasts a capacity of 115 MW, utilizing the strong winds in Patagonia for electricity generation.
- Hydropower: Rapel Hydropower Plant holds the title with a capacity of 570 MW, leveraging the water flow of the Rapel River.
Highest Annual Electricity Generation:
- Solar: El Romero photovoltaic (PV) solar farm generated the most electricity in 2022, producing 2,922 GWh. It sprawls across the Atacama Desert, harnessing abundant sunshine.
- Wind: Renaico Wind Farm holds the wind record for 2022, generating 2,134 GWh with its multiple wind turbines.
- Hydropower: Rapel Hydropower Plant maintains its lead here as well, generating 8,935 GWh in 2022 due to its large capacity and consistent water flow.
Considerations:
- CSP plants like Cerro Dominador offer dispatchable energy (available on demand) unlike PV farms, but their capacity is smaller.
- Wind farms can have variable generation depending on wind speeds, while hydropower offers more stable generation but faces environmental considerations.
- Annual generation can vary based on weather conditions and plant maintenance schedules.
There's no single "largest" renewable energy power plant in Chile with different metrics leading to various answers. Cerro Dominador holds the solar capacity title, Rapel leads in hydropower, while El Arrayán boasts the highest wind capacity. El Romero and Rapel generated the most solar and hydropower electricity in 2022, while Renaico reigns supreme in wind generation for that year. Understanding these distinctions can provide a clearer picture of Chile's diverse renewable energy landscape!
Renewable Energy Company in Chile
Leading Renewable Energy Companies in Chile:
Chile's booming renewable energy sector attracts numerous companies. Here are some prominent players:
1. Mainstream Renewable Power:
- Origin: Ireland
- Focus: Development, financing, construction, and operation of wind and solar farms
- Chilean Portfolio: Over 1.4 GW of operating and under-construction projects
2. Aconcagua Energía:
- Origin: Spain
- Focus: Development and operation of solar and wind farms, transmission lines, and battery storage solutions
- Chilean Portfolio: Over 1 GW of operating solar and wind farms
3. Voltalia:
- Origin: France
- Focus: Global leader in development and operation of renewable projects across 18 countries
- Chilean Portfolio: Over 800 MW of operating solar and wind farms
4. AES Andes:
- Origin: United States
- Focus: One of the largest electricity generators in Chile with thermal, hydro, solar, and wind power plants
- Chilean Portfolio: Over 2.5 GW of renewable energy capacity
5. Engie:
- Origin: France
- Focus: Multinational utility company with involvement in solar, wind, geothermal, and biomass projects
- Chilean Portfolio: Over 1 GW of operating solar and wind farms
Additional Notes:
- This list isn't exhaustive, and numerous other companies contribute to Chile's renewable energy landscape.
- The Chilean renewable energy market continues to grow, attracting new players and investments.
- The growth of renewables benefits the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and creates jobs for the Chilean economy.
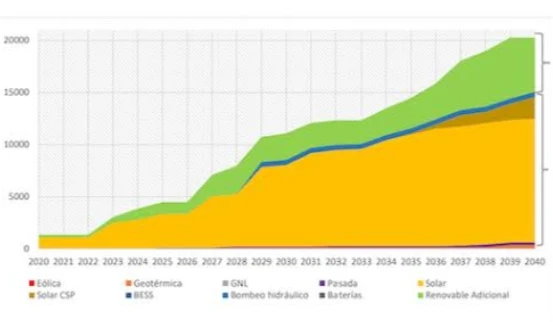
Future of Renewable Energy Development in Chile
Predicting the future is often fraught with uncertainty, but based on trends and existing plans, here's a possible glimpse into the future of renewable energy development in Chile:
Increased Capacity and Diversification:
- Ambitious Targets: Chile aims to achieve 70% renewable energy generation by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2050, necessitating a significant increase in renewable energy capacity.
- Beyond Solar and Wind: While solar and wind will likely remain dominant, further development of other renewables like geothermal, biomass (with sustainability considerations), and marine energy could contribute to a more diverse mix.
Technological Advancements:
- Innovation Focus: Continued research and development in areas like solar cell efficiency, larger wind turbines, advanced energy storage solutions, and green hydrogen production will be crucial for enhancing performance and affordability.
- Smart Grid Integration: Optimizing grid operations and integrating intermittent renewables effectively will require advanced smart grid technologies and data analytics.
Policy and Investment Landscape:
- Evolving Policy Framework: Government policies are expected to continue evolving, supporting technological advancements, addressing grid challenges, and ensuring social and environmental sustainability.
- Attracting Investment: Maintaining a stable and investor-friendly environment will be crucial for securing the necessary funds to achieve ambitious goals.
Community and Social Considerations:
- Community Engagement: Active participation and addressing concerns of communities affected by renewable energy projects will be vital for long-term social acceptance and sustainability.
- Just Transition: Ensuring a fair and equitable transition away from fossil fuels and supporting affected communities will be crucial for achieving widespread support.
Challenges and Uncertainties:
- Climate Change Impacts: Adapting to potential climate-related challenges like droughts and extreme weather events will require resilience planning and diversification of renewable sources.
- Technological Progress: The pace of technological advancements and cost reductions in various renewable technologies will influence the future development path.
- Geopolitical and Economic Factors: Global economic and political fluctuations could impact investment flows and resource availability.
Conclusion:
Chile's future in renewable energy development appears promising, fueled by ambitious goals, strong political will, and a favorable environment. However, navigating challenges and uncertainties will be crucial. By fostering innovation, ensuring sustainability, and prioritizing social aspects, Chile has the potential to solidify its position as a global leader in the renewable energy transition, inspiring other nations on the path towards a clean and sustainable future.